Quality control involves operational techniques meant to ensure quality standards. This includes identifying, analyzing, and correcting problems. While quality assurance occurs before a problem is identified, quality control is reactionary and occurs after a problem has been identified. Quality control monitors specific project outputs and determines compliance with applicable standards. It also identifies project risk factors, and their mitigation, and looks for ways to prevent and eliminate unsatisfactory performance.
Quality control is responsible for monitoring the project outputs according to the applicable standards of the project. In addition to that, it also determines the project risk factors, their mitigation, and measures to prevent and eliminate unsatisfactory performances.
Quality Control (QC) refers to quality-related activities associated with the creation of project deliverables. Quality control is used to verify that deliverables are of acceptable quality and that they are complete and correct. Examples of quality control activities include inspection, deliverable peer reviews, and the testing process. Quality control monitors project deliverables to verify that the deliverables are of acceptable quality and the customer is satisfied. The focus of quality control is on the deliverables of the project.
Quality control is a tip of quality management. As a rule, it’s observed even when the rest of quality management is overlooked. This product-oriented quality management component starts simultaneously with software development. QC includes software testing activities predetermined by a quality plan. Manual and automated functionality, performance, integration, usability, security, regression testing – all these and many other testing types comprise QC. Quality control should check whether the software is compliant with its requirements and whether no severe defects will be revealed after the software is released.
Software Quality Control is a validation activity, where the quality of the developed software product meets the client’s need and exceptions or fits for purpose i.e.to checking if we have built the right software or not. This process deals with product-oriented to find the defect and improve the developed software product quality. Software product testing by executing the application code is part of software quality control.
Software Quality Control Activities
The software quality control process mainly deals with software products, development processes, and resources. It works on PDCA (Plan Do Check Action) principle.
The software quality control process mainly deals with two activities with some sub-activities.
1. Review Activities (Quality Assurance (QA)
The Review Activities of the software quality control process are as follows:
Review Activities
-
Requirements Review
-
Design Review
-
Coding Review
-
Test Plan Review
-
Test Cases Review
-
Deployment Review
The Review Activity is one type of static testing or verification process of the software documents to prevent defects. It is process-oriented to improve the development process performed without program execution. The requirement document and design review are part of it. It has multiple review activities like requirements, design, coding, test plan, test cases, and deployment within the software development life cycle process. This is a process-level verification to prevent defects in the software application documents.
2. Testing Activities (Quality Control (QC))
The Testing Activities of the software quality control process are as follows:
Testing Activities
-
Unit Testing
-
Integration Testing
-
System Testing
-
Acceptance Testing
-
Release Testing
-
Maintenance Testing
The Testing Activity is a type of Dynamic in nature or validation process of the software application to find the defects. It has product-oriented to enhance the software product quality, performed with program execution. Product testing is the main part of it and has multiple testing activities like unit, integration, system, acceptance, release, and maintenance testing phases within the software development life cycle process.
In this activity, we also use some extra functional levels of testing like smoke testing, sanity testing, retesting, regression testing, and some non-functional testing like performance testing, stress testing, load testing, volume testing, and endurance testing to improve the priority (urgency of fix the defect) and severity (Impact of the defect) of the developed software product quality. So the QA (verification) and QC (validation) processes are internally related to the software quality control improvement process.
Software Quality Control (SQC) ensures the task of achieving and maintaining the quality of a software product. It may be seen as a set of activities that are being carried out with the aim of achieving quality from each different perspective in a software product. These activities may consist of tracing, identifying, removing, and correcting the maximum number of possible bugs or defects in the software. In short, SQC consists of different testing activities along with some other activities, comprehensively to control and achieve the desired level of quality in a product.
So, Software Quality Control (SQC) = Software Quality Assurance (SQA)?
Although both SQC and SQA are being carried out in the direction of achieving quality attributes in a software product, still they are not the same. SQA concerns with the pre-development and ongoing development process whereas SQC is usually a post-development process. SQA ensures the appropriate standards and correct procedures for developing the desired quality of software, while SQC corrects the developed software (if required) to improve & enhance its quality. Thus, it may be interpreted that SQA is process-oriented and SQC is product oriented.
The below diagram shows the working of the testing activities with a detailed explanation:

Unit Testing
The testing of the smallest independently executable parts /units/components of the software application. It is also known as component testing. It is done by the development team early in the development stage.
Integration Testing
In this testing, to find the defects or bugs in interfaces or interactions between components/units i.e. to test whether the combined units are works or not. It is done by the Technology/Development Lead not by Testers. There are two approaches to Integration Testing i.e. Top-Down and Bottom-Up approaches.
Here test drivers and test stubs are used to assist the integration testing workflow. When there are temporary programs in the applications to substitute programs in development, are called stubs and drivers. The main program if replace is called a Driver and if the lower programs are replaced, then it is called Stubs. When we have stubs and drivers, we call the environment as Test Harness.
System Testing
Once the deployment team sends a mail that the software is installed into the test environment. We start with build verification testing (Smoke test). Here we check if the minimum features are working and send a mail to the development team that we are accepting or rejecting the build. It is also called end-to-end testing and is performed by the testing team in the testing environment. When two or more applications need to operate together, there is one more level of testing between system testing and user acceptance testing is called system integration testing.
Acceptance Testing / User Acceptance Testing
The objectives of this testing are:
-
To gain confidence for release.
-
To check if the software is fit for the purpose.
-
Checking the software from a business point of view.
It is performed by the client. It has two types Alpha Testing and Beta Testing. The Alpha Testing is called Business Acceptance Testing (BAT) or Factory Level Testing, performed by the client in the development organization site. Beta Testing is called Product Verification Testing (PVT) or Field Level Testing, performed by the client in the place where the software is being used.
Release Testing
Release testing is the final testing phase of a software product or application to verify, the developed software to be released. Here the entire functionalities of that application should be tested to ensure the readiness of the software application.
Maintenance Testing
The testing of the software which is in production, when there are changes to either the (i.e. defects or modifications) software or to the environment. In this phase, we plan on Impact Analysis i.e. the change control board (CCB) would be a group of architects, designers, developers, and testers, who can judge the impact of change asked by the client i.e. change request (CR). It is also helpful for testing as it guides where to do most of the testing i.e. retesting and regression testing. This type of testing is done by the testers.
Software Quality Control Standards
There are some ISO standards to review/describes the quality of the software-developed product. The ISO/IEC/IEEE has proposed a number 29119 for international standards in software quality control, which is followed by the software development life cycle (SDLC) model of the development process. It has mainly five international levels of software quality control (QC) standards and some sub-standards to review both the process level & product level of the application.
They are as follows:
1. International Software QC Standards
-
ISO/IEC 29119-1: It indicates the concepts and definitions of software.
-
ISO/IEC 29119-2: It indicates the different test processes in a software product.
-
ISO/IEC 29119-3: It deals with testing related documents of the software application.
-
ISO/IEC 29119-4: It describes the different testing techniques and plans for that software product.
-
ISO/IEC 29119-5: It deals with different types keyword driven software testing.
2. Auxiliary Software QC Standards
-
IEEE 730: It deals with software product verification i.e. Quality Assurance (QA).
-
IEEE 830: It describes the accurate development of software applications with proper requirements.
-
EEE 1008: This standard deals with unit testing of the developed application.
-
IEEE 1012: It deals with the verification and validation of applications.
-
IEEE 1028: This standard deals with proper software application inspection purposes.
-
IEEE 1044: It is used to check some inconsistencies in application software.
-
IEEE 1059: It deals with application-guiding verification and validation.
-
IEEE 1061: This standard is used for the better quality of software product development i.e. to deal with application quality metrics.
-
IEEE 12207: It is used for used development life cycle processes of applications.
Software Quality Control Techniques
Quality control is a process followed by the IT organization to develop extremely quality software products and improve the organization’s productivity as well as the goals of the software products. There are multiple techniques/methods for software quality control of software applications, but the PDCA (Plan Do Check Action) technique is one of the best approaches to software quality control.
-
Goal Question Centric Model
-
Overall Risk Management Model
-
The PDCA Model
-
Overall Software Quality Control Model
-
Quality Control by Spiral Model
-
Control Management Model
1. Goal Question Centric Model
The Software Quality Control Goal Question Centric Model (GQM) is a model used to evaluate and measure software quality. The GQM model provides a systematic approach to defining, measuring, and improving software quality by focusing on the goals, questions, and metrics that are relevant to the stakeholders.
The steps involved in the GQM model include:
-
Identify Goals: This involves identifying the goals and objectives of the software product and the stakeholders who will be impacted by the software quality.
-
Formulate Questions: This involves formulating questions that will help to understand the impact of software quality on the stakeholders and the goals.
-
Define Metrics: This involves defining the metrics that will be used to measure software quality and answer the questions.
-
Collect Data: This involves collecting data on software quality metrics through testing, inspection, and other evaluation methods.
-
Analyze Data: This involves analyzing the data to determine the impact of software quality on the stakeholders and the goals.
-
Make Decisions: This involves making decisions based on the results of the analysis and taking appropriate action to improve software quality.
-
Continuously Evaluate and Improve: This involves continuously evaluating and improving software quality through the GQM model to ensure that software products meet the needs and expectations of customers.
The GQM model provides a comprehensive and systematic approach to software quality control, enabling organizations to measure software quality in a meaningful and relevant way. By focusing on the goals, questions, and metrics that are relevant to stakeholders, the GQM model helps organizations deliver high-quality software products that meet the needs and expectations of customers.
2. Overall Risk Management Model (ORMM)
The Software Quality Control Overall Risk Management Model (ORMM) is a model used to identify, evaluate, and manage risks in software development. The ORMM provides a systematic approach to managing risks in software development by focusing on the identification, analysis, and control of risks.
The steps involved in the ORMM include:
-
Identify Risks: This involves identifying the potential risks that could impact software quality and development.
-
Analyze Risks: This involves analyzing the potential impact of risks on software quality and development, including the likelihood and severity of the risk.
-
Prioritize Risks: This involves prioritizing the risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, with a focus on the risks with the highest potential impact.
-
Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies: This involves developing strategies to mitigate the risks, including contingency plans and risk mitigation activities.
-
Implement Risk Mitigation Strategies: This involves implementing risk mitigation strategies to reduce the impact of risks on software quality and development.
-
Monitor and Review Risks: This involves monitoring and reviewing the risks on a regular basis to ensure that the risk mitigation strategies are effective and to identify any new risks that may arise.
The ORMM provides a comprehensive and systematic approach to software quality control and risk management, enabling organizations to identify, evaluate, and manage risks in software development. By focusing on the identification, analysis, and control of risks, the ORMM helps organizations to reduce the risk of defects, improve the overall quality of software products, and increase customer satisfaction.
3. PDCA Model
It stands for the Plan-Do-Check-Action model. It is one of the simplest models of the software development process through which the quality control of the application is done from the initial stage of development. The parameters like product/application, processes, and resources are influences the quality control of the software application.
It contains four phases:
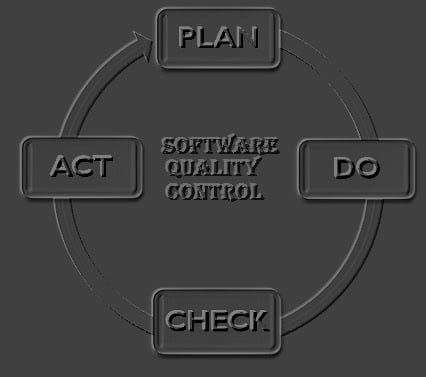
1. Plan: During this initial phase the software quality control processes are initiated or planned. Here to set standard software quality goals and plan accordingly to get it.
2. Do: In this phase start developing the software application according to the project plan parameters to execute it i.e. work in progress state.
3. Check: In this phase is dedicated to the static and dynamic testing of the developed software application to find defects to improve the quality of the product. Here we validate the excepted output values with actual parameter values.
4. Action: During this phase, the corrective actions take place to remove bugs or issues from the developed software product i.e. the bugs are fixed and the rework action has been done if needed.
4. Overall Software Quality Control Model (OSQCM)
The Overall Software Quality Control Model (OSQCM) is a framework used to plan, implement, and evaluate software quality control activities. The OSQCM provides a systematic approach to software quality control by focusing on the key processes and activities involved in software development.
The steps involved in the OSQCM include:
-
Plan Software Quality Control: This involves defining the quality control objectives, standards, and procedures to be used during software development.
-
Conduct Reviews and Inspections: This involves evaluating software products through code reviews, walkthroughs, and other formal inspection techniques to identify defects and potential quality issues.
-
Perform Testing: This involves executing tests (e.g., unit tests, integration tests, system tests) to identify and validate defects in software products.
-
Monitor and Measure Software Quality: This involves monitoring and measuring software quality metrics (e.g., defect density, test coverage) to determine the overall quality of software products.
-
Report and Correct Defects: This involves reporting defects in software products and working to correct them in a timely manner.
-
Continuously Improve Software Quality: This involves continuously monitoring and improving the software quality control process to ensure that it is effective and efficient.
The OSQCM provides a comprehensive and systematic approach to software quality control, enabling organizations to plan, implement, and evaluate software quality control activities in a consistent and efficient manner. By focusing on the key processes and activities involved in software development, the OSQCM helps organizations to deliver high-quality software products that meet the needs and expectations of customers.
5. Quality Control by Spiral Model
The Quality Control by Spiral Model is a software development process that combines elements of both the waterfall model and the iterative model. The spiral model is used for managing software projects that involve significant uncertainty, risk, and change.
The spiral model involves four main phases:
-
Planning: This phase involves defining the objectives and scope of the software project, identifying the risks, and developing a plan for managing the project.
-
Risk Analysis: This phase involves evaluating the risks associated with the software project and determining the strategies for mitigating these risks.
-
Engineering: This phase involves developing and testing a prototype of the software product. The prototype is used to validate the design and evaluate the risks associated with the software project.
-
Evaluation: This phase involves evaluating the results of the software project and determining the next steps. This may involve revising the project plan, starting over with a new iteration of the spiral, or moving forward with the development of the final product.
The spiral model provides a flexible and iterative approach to software development, enabling organizations to manage uncertainty and risk throughout the development process. By focusing on the iterative development of prototypes, the spiral model helps organizations to reduce the risk of defects and improve the overall quality of software products.
6. Control Management Model
Software Quality Control Management Model refers to a systematic approach to managing and improving the quality of software products. This model includes various processes, activities, and techniques for ensuring that software products meet the required quality standards.
The key elements of a software quality control management model include:
-
Quality Planning: This involves defining the quality objectives, standards, and procedures that will be used to evaluate software products.
-
Quality Control: This involves implementing the quality control processes and techniques that are used to evaluate software products, including code reviews, inspections, testing, and monitoring of software quality metrics.
-
Quality Assurance: This involves ensuring that the quality control processes and techniques are being applied effectively and efficiently throughout the software development process.
-
Quality Improvement: This involves continuously monitoring and improving the software quality control processes and techniques to ensure that they are effective and efficient.
The software quality control management model provides a systematic approach to managing and improving the quality of software products. By focusing on the key processes and activities involved in software development, the model helps organizations deliver high-quality software products that meet the needs and expectations of customers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Software Quality Control
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages:
-
Advantages
Below are the advantages
-
It is used to validate the software application as per the client’s needs and exceptions.
-
The software QC is used to identify the defects in the software application.
-
It improves the productivity of the software development team as well as software product quality.
-
It enhances the organizational ability to produce a high-quality software product.
-
It makes the final software product ready for delivery.
-
Increased the build trust in project management and future-level development.
-
It is used to reduce the re-development or re-work cost as the Software QC will impose from the scratch level of the development phase.
-
It boosts customer satisfaction and efficiency of the software product.
-
It is a reactive approach and a separate testing team will involve finding defects.
-
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages
-
It requires more time-consuming process testing.
-
The deployment of a software product should be delayed.
-
It needs more resources for software product validation.
-
Each individual on the team doesn’t take responsibility for the quality of their own work.
-
If the software application is rejected, then there is a big issue in budgeting for the organization.
Conclusion
In this article, we discuss the software quality control process to develop the development build trust, identify defects, prevent defects, and ensure the quality of the software product. It also describes the different international software quality control standards with activities and methods related to them. As it is a reactive approach to ensure the developed software product meets the client’s exceptions and standard quality or not. It involves multiple testing phases to develop the standard product quality and improve the development process in the software development life cycle process. Thus, it is a final step to check the software product before delivery.
Although, SQA is essential for the development process but it may not guarantee the maximum possible quality of the product as it is limited to process and procedures, but through SQC, we may be assured of attaining maximum quality as it directly works on the software product to remove any defects or bugs that may occur in the software product, even after the implementation of SQA.
